There are two types of loops available in python
while loop
Using the while loop we can execute a set of statements as long as a condition is true. It tests the condition before the loop body is executed.
for loop
A for loop is used for iterating over a sequence (that can be a list, a tuple, a dictionary, a set, or a string).
A for loop is used to execute a sequence of statements multiple times and reduces the amount of code that manages the loop variable.
Loop Control statements
A Loop control statement changes the execution from the normal sequence.
Python supports the following control statements.
break statement
Terminates the loop statement and transfers execution to the statement immediately following the loop.
continue statement
Causes the loop to skip the remainder of its body and immediately retest its condition prior to reiterating.
pass statement
For loops cannot be empty, but if you for some reason have no content in a for loop you can put in the pass statement to avoid getting an error.
Lets look an example of the for loop
#!/usr/bin/python
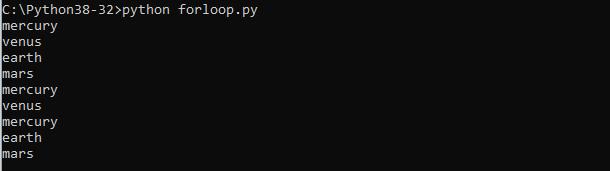
planets = ("mercury", "venus", "earth", "mars")
for x in planets:
print(x)
#using the break statement
for x in planets:
print(x)
if x == "venus":
break
#using the continue statement
for x in planets:
if x == "venus":
continue
print(x)
Save the script and run it and you see something like this
Now lets look at similar while loop examples
#!/usr/bin/python
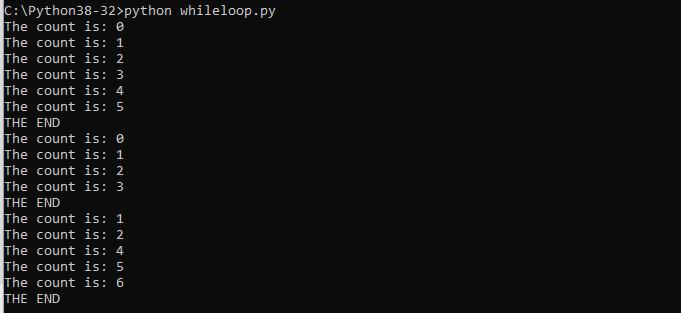
count = 0
while (count <= 5):
print ('The count is:', count)
count = count + 1
print ("THE END")
#using break
count1 = 0
while (count1 <= 5):
print ('The count is:', count1)
if count1 == 3:
break
count1 += 1
print ("THE END")
#using continue
count2 = 0
while (count2 <= 5):
count2 += 1
if count2 == 3:
continue
print ('The count is:', count2)
print ("THE END")
Save the script and run it and you see something like this

![Java SE 11 Programmer I [1Z0-815] Practice Tests](https://static.shareasale.com/image/43514/728X909.jpg)



![Java SE 11 Developer (Upgrade) [1Z0-817]](https://static.shareasale.com/image/43514/728X9033.jpg)
![Java SE 11 Programmer II [1Z0-816] Practice Tests](https://static.shareasale.com/image/43514/728X9026.jpg)