In this code example we will create a simple clock. There will be a console based example and a simple gui version as well.
We will use the datetime module which provides classes for manipulating dates and times.
We will use the strftime() which has a method for formatting date objects into easily readable strings, it takes one parameter, which is a format code which is used to specify the format of the returned string.
We will use the following format codes, there are many others available.
%H Hour 00-23 %p AM/PM %M Minute 00-59 %S Second 00-59
Command line example
#!/usr/bin/env python
import datetime
now = datetime.datetime.now()
print (now.strftime("%H:%M:%S %p"))
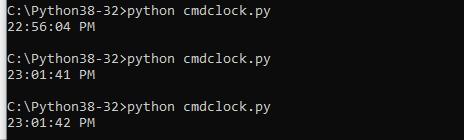
If you run this example you will see something like this. This shows several runs.
Gui Example
Now we will create a gui example, for this we will use tkinter
#!/usr/bin/env python
import tkinter
# retrieve the system time
from time import strftime
top = tkinter.Tk()
#title of the App
top.title('Digital Clock')
#restric the resizable of the gui window
top.resizable(0,0)
def time():
string = strftime('%H:%M:%S %p')
clock.config(text = string)
clock.after(1000, time)
#black background with yellow text
clock = tkinter.Label(top, font = ('arial', 40, 'bold'), background = 'black', foreground = 'yellow')
clock.pack(anchor = 'center')
time()
top.mainloop()
If you run this example you will see a gui that looks something like this


![Java SE 11 Programmer II [1Z0-816] Practice Tests](https://static.shareasale.com/image/43514/728X9026.jpg)

![Java SE 11 Developer (Upgrade) [1Z0-817]](https://static.shareasale.com/image/43514/728X9033.jpg)

![Java SE 11 Programmer I [1Z0-815] Practice Tests](https://static.shareasale.com/image/43514/728X909.jpg)
